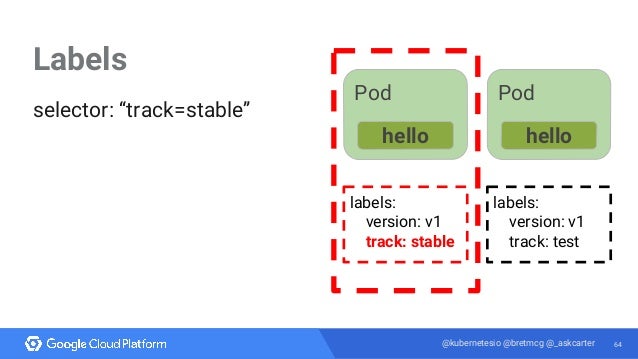
44 labels and selectors in kubernetes
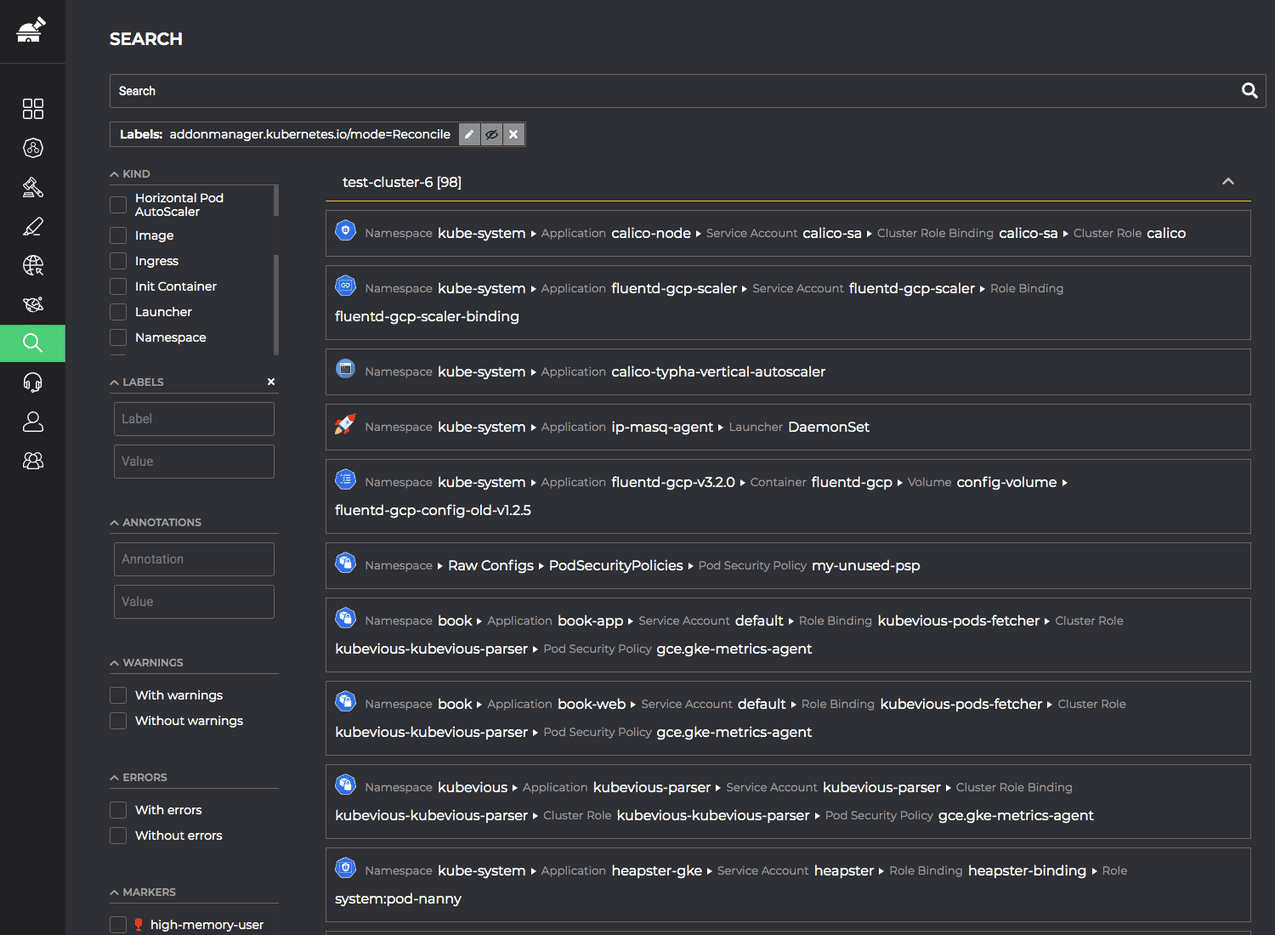
Kubernetes Core Concepts - Labels, Selectors and Annotations What are Selectors in Kubernetes? Selectors are used to filter out objects based on their assigned Labels. Labels and Selectors goes hand in hand. For example Selectors will help us filter out objects like give all the application pods which are of type staging. Example syntax to define Selectors Learn about Label and Selector in Kubernetes - Huong Dan Java The first thing is that we can define the Label in the spec file that defines the information of a Kubernetes object. In which key1:value1, key2:value2 are the value pairs that we want to assign to the Kubernetes object. For example, if I want to run a Pod with the Label assigned to this Pod, I will define the spec of Pod as follows:
Kubernetes - Labels & Selectors - tutorialspoint.com Labels selector are core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. They are used by the users to select a set of objects. Kubernetes API currently supports two type of selectors − Equality-based selectors Set-based selectors Equality-based Selectors They allow filtering by key and value. Matching objects should satisfy all the specified labels.
Labels and selectors in kubernetes
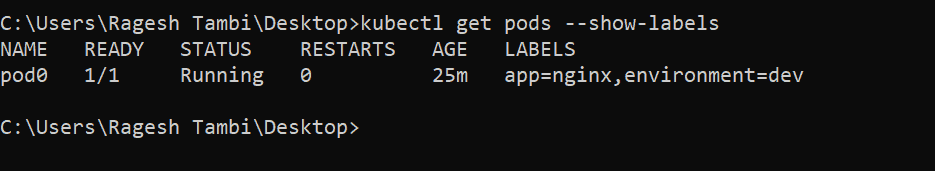
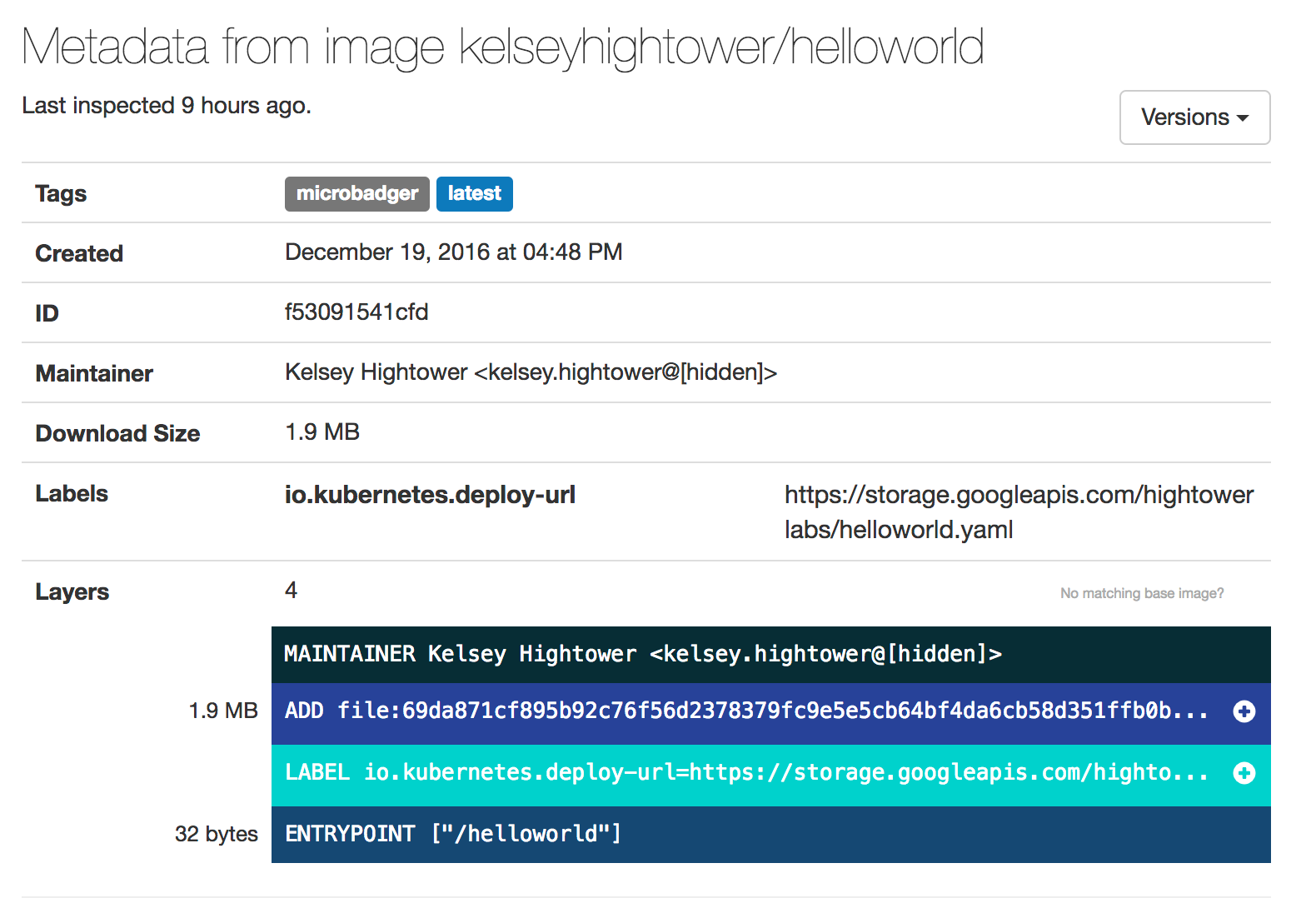
A Kubernetes Guide for Labels and Selectors | Datree.io Labels can be used by both Kubernetes and homo-sapiens to organize and to select subsets of objects. When dealing with Kubernetes config files, labels are always added under the "metadata" section of the manifest. Labels vs annotations Annotations are also key-value pairs that are attached to objects and are used to describe Kubernetes resources. Labels and Selectors - Kubernetes - GitLab The label selector is the core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. The API currently supports two types of selectors: equality-basedand set-based. A label selector can be made of multiple requirementswhich are comma-separated. In the case of multiple requirements, all must be satisfied so the comma separator acts as a logical AND(&&) operator. Civo Academy - Learn about pod labels and selectors - Civo.com In this video, we'll be discussing labels and selectors. Now, labels in Kubernetes are a set of key-value pairs attached to a Kubernetes object such as pods. It is basically used to provide attributes to create a meaningful Kubernetes object. So, the command to view the labels is kubectl get pods --show-labels. Labeling a pod
Labels and selectors in kubernetes. Kubernetes Labels & Selectors - Kubernetes - Wisdom Jobs Labels selector are core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. They are used by the users to choose a set of objects. Kubernetes API currently supports two type of selectors − Equality-based selectors Set-based selectors Equality-based Selectors They let filtering by key and value. Matching objects should please all the stated labels. Labels and Selectors — Kubernetes on AWS 0.1 documentation Labels and Selectors ¶ Labels are key/value pairs that are attached to Kubernetes objects, such as pods (this is usually done indirectly via deployments). Labels are intended to be used to specify identifying attributes of objects that are meaningful and relevant to users. Labels can be used to organize and to select subsets of objects. Working with labels and selectors | Kubernetes Cookbook - Packt Working with labels and selectors Labels are a set of key/value pairs, which are attached to object metadata. We could use labels to select, organize, and group objects, such as Pods, ReplicaSets, and Services. Understanding Labels, Selectors and Annotations in Kubernetes There are two kinds of selectors. Equality-based and Set-based selectors. Equality-based requirement Equality based selectors help you filter resources equal to a certain key and value. You would following operators for equality based-requirements: = == != Example # this command would give us all resources with the env =prod label
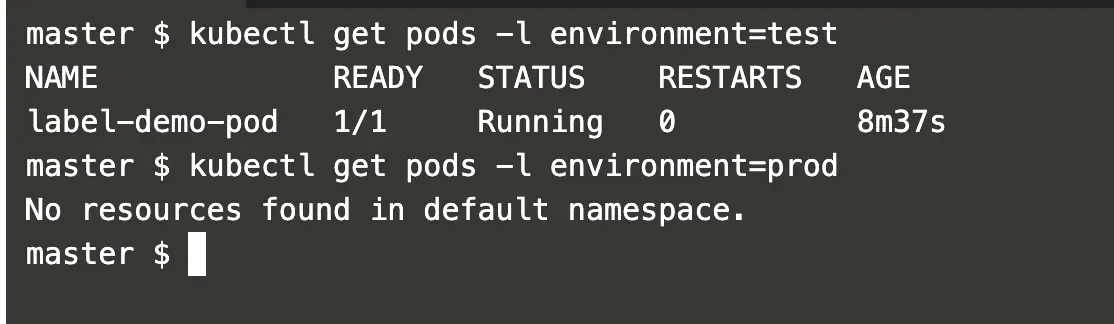
Kubernetes, Labels and Selectors - Automated Ramblings The replica controller could only find 3 pods running using the matchLabel selector after we changing the run label on pod web-internal-6b444b6dd9-kd8w2 and deployed another pod to remediate the issue. Labels and selectors have many additional uses to the one covered in this post; they are a core part of the Kubernetes platform. Labels and Selectors in Kubernetes - HowtoForge To get Pods matching a label of our choice, we can "--selector" in the command as follows. kubectl get pods --selector environment=test kubectl get pods --selector app=nginx We can also use "-l" instead of "--selector" to get the Pods matching the label of our choice. kubectl get pods -l environment=test kubectl get pods -l environment=prod Kubernetes labels, selectors & annotations with examples Labels give us another level of categorization, which becomes very helpful in terms of everyday operations and management. Labels are attached to Kubernetes objects and are simple key: value pairs. You will see them on pods, replication controllers, replica sets, services, and so on. Labels and Selectors | Kubernetes The label selector is the core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. The API currently supports two types of selectors: equality-based and set-based . A label selector can be made of multiple requirements which are comma-separated. In the case of multiple requirements, all must be satisfied so the comma separator acts as a logical AND ( &&) operator.
Labels - Unofficial Kubernetes - Read the Docs The kubernetes.io/ prefix is reserved for Kubernetes core components. Valid label values must be 63 characters or less and must be empty or begin and end with an alphanumeric character ... Labels selectors for both objects are defined in json or yaml files using maps, and only equality-based requirement selectors are supported: "selector ... Using Kubernetes Annotations, Labels, and Selectors - How-To Geek Annotations, labels, and selectors are used to manage metadata attached to your Kubernetes objects. Annotations and labels define the data while selectors provide a way to query it. Here are the differences between the three concepts, what they're designed for, and how you can use them to manage your resources. Annotations Kubernetes Selector | How does Selector Works in Kubernetes? - EDUCBA 1. Label Selector. We apply labels to the Kubernetes objects to organize or select a group of objects. Labels can be attached at creation time or added and modified at any time. Labels are case sensitive. We can use Label Selector using the option '-l'. Let's create three pods with labels "env: prod" and "app: nginx-web" and two ... Labels | Kubernetes Platform - Kube by Example kubectl get pods --selector owner=michael. The --selector option can be abbreviated to -l, so selecting pods that are labelled with env=development can also be done using: kubectl get pods -l env=development. Oftentimes, Kubernetes objects support set-based selectors. Let's launch another pod that has two labels (env=production and owner=michael):
Using K8s Label Selectors in Go without doing it wrong Using labels.Selector. The labels.Selector interface is located in the apimachinery repo under pkg/labels/selector.go.It's used to read and query Kubernetes Objects via their labels. You should ...
Labels and Selectors - Kubernetes The label selector is the core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. The API currently supports two types of selectors: equality-based and set-based . A label selector can be made of multiple requirements which are comma-separated. In the case of multiple requirements, all must be satisfied so the comma separator acts as a logical AND ( &&) operator.
Learn Kubernetes Labels By Following Examples | Densify Kubernetes labels example use cases. Now that we've covered the basics of working with K8s labels, let's take a look at some common use cases. Services and Deployments. The most common use case for labels is using label selectors in Kubernetes services and deployment objects. A service object targets pods based on label selectors.
Kubernetes Labels | Labels And Annotations In Kubernetes - K21Academy Label selectors are used for filter Kubernetes objects based on a set of labels. Selectors use a simple Boolean language. There are two kinds of selectors: Equality based and Set based. Equality based. Equality-based selectors allow filtering by label keys and values. Three kinds of operators are used: =, ==, != Example: If we wanted to list ...

What I learned about Kubernetes - (Scheduling - Manual Scheduling, Labels and Selectors) ~ Root ...
Kubernetes Labels, Selectors, and Annotations | Getting Started - ContainIQ As their name suggests, label selectors allow you to identify the objects you have tagged with particular labels. Label selectors can either be equality-based or set-based. Equality-based label selectors work by specifying an exact value that you want to match against.
Kubernetes: Usage and Understanding of Kubernetes Labels ... - Medium Labels are key/value pairs that are attached to objects, such as pods. Labels are intended to be used to specify identifying attributes of objects that are meaningful and relevant to users. Labels can be attached to objects at creation time and subsequently added and modified at any time Each object can have a set of key/value labels defined.
The Purpose of Labels and Selectors in Kubernetes kubernetes The Purpose of Labels and Selectors in Kubernetes Logically isolate and group objects inside of Kubernetes with loose coupling. Justin VanWinkle 15 Jan 2021 • 1 min read In short, labels are a way to group and reference an object. For instance, you could group all APIs with a label like type: api.
6. Labels, annotations, selectors — Kubernetes Tasks 0.1 documentation Create service (only routable inside cluster). The service is assigned Cluster IP (DNS record is automatically created) which load-balance across all of the pods that are identified by the selector. $ kubectl expose deployment app1-prod.
What is the difference between Label and Selector in kubernetes? Via a label selector, the client/user can identify a set of objects. The label selector is the core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. In a nutshell label selectors depend on labels to select a group of resources such as pods. For example a deployment selects a group of pods by a label selector in the deployment spec. Share
How to Provision Node Labels and Selectors in Kubernetes? (K8s) Labels selectors are core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. They are used by the users to select a set of objects. Kubernetes API currently supports two types of selectors − Equality-based...
Civo Academy - Learn about pod labels and selectors - Civo.com In this video, we'll be discussing labels and selectors. Now, labels in Kubernetes are a set of key-value pairs attached to a Kubernetes object such as pods. It is basically used to provide attributes to create a meaningful Kubernetes object. So, the command to view the labels is kubectl get pods --show-labels. Labeling a pod
Labels and Selectors - Kubernetes - GitLab The label selector is the core grouping primitive in Kubernetes. The API currently supports two types of selectors: equality-basedand set-based. A label selector can be made of multiple requirementswhich are comma-separated. In the case of multiple requirements, all must be satisfied so the comma separator acts as a logical AND(&&) operator.
A Kubernetes Guide for Labels and Selectors | Datree.io Labels can be used by both Kubernetes and homo-sapiens to organize and to select subsets of objects. When dealing with Kubernetes config files, labels are always added under the "metadata" section of the manifest. Labels vs annotations Annotations are also key-value pairs that are attached to objects and are used to describe Kubernetes resources.










Post a Comment for "44 labels and selectors in kubernetes"